Amino Acids & Derivatives for Peptide Synthesis
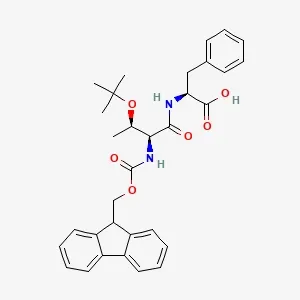
Fmoc-Ser(tBu)-Gly-OH
Specially formulated for precision peptide synthesis, Fmoc-Ser(tBu)-Gly-OH (CAS No. 81672-17-5) is a protected dipeptide intermediate offering excellent purity (99% min) and structural stability. It appears as a white to light yellow solid, with a molecular formula of C₂₄H₂₈N₂O₆ and a molecular weight of 440.5 g/mol. With defined thermal properties and refrigeration storage requirements, this compound is particularly suitable for temperature-sensitive processes in pharmaceutical research and peptide manufacturing.
- CAS No.: 81672-17-5
- Molecular Formula: C₂₄H₂₈N₂O₆
- Purity: 99% min




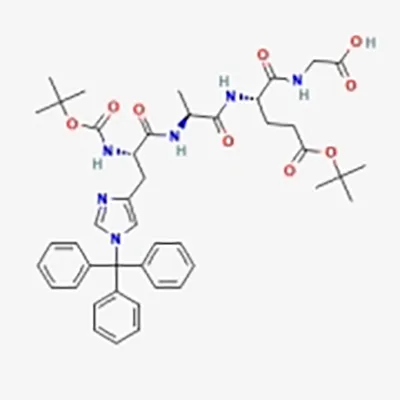
![Fmoc-Gly-Ser[PSI(Me,Me)pro]-OH](products/2-4-8-fmoc-gly-ser-psi-me-me-pro-oh_01.webp)
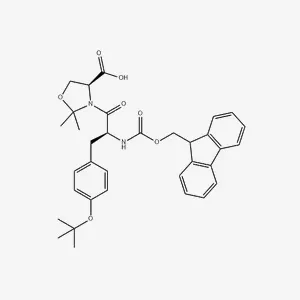
![Fmoc-Ser(tBu)-Ser[Psi(Me,Me)Pro]-OH](products/2-4-11-fmoc-ser-tbu-ser-psi-me-me-pro-oh_01.webp)
![Fmoc-L-Lys[C₂₀-OtBu-γ-Glu(OtBu)-AEEA]-OH](products/2-4-1-fmoc-l-lys-C20-otbu-glu-otbu-aeea-oh_01.webp)
![Fmoc-Lys[γ-Glu(OtBu)-C₁₈-OtBu)]-OH](products/2-4-2-fmoc-lys-glu-otbu-c18-otbu-oh_01.webp)