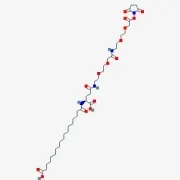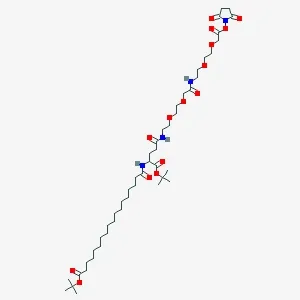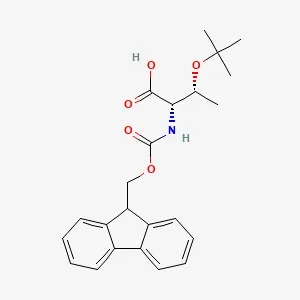
Amino Acids & Derivatives for Peptide Synthesis
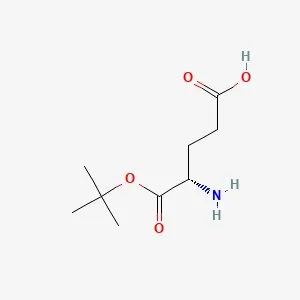
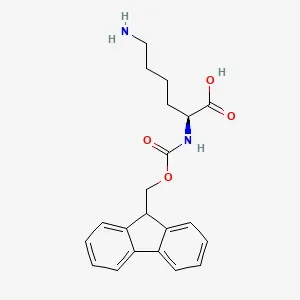
Fmoc-L-Thr(tBu)-OH
Fmoc-L-Thr(tBu)-OH (CAS No. 71989-35-0), also known as N-Fmoc-O-tert-butyl-L-threonine, is a protected amino acid widely used in solid-phase peptide synthesis. It contains a Fmoc group shielding the α-amino function and a tert-butyl group protecting the hydroxyl side chain, allowing selective deprotection during synthesis. This compound plays a key role in assembling GLP-1 analogs such as Semaglutide and Tirzepatide. Offered as a white crystalline powder with 99% min purity, it has a molecular weight of 397.5 g/mol and formula C₁₈H₂₃NO₅. Proper storage at 2–8 °C in a sealed container is recommended to maintain stability.
- CAS No.: 71989-35-0
- Molecular Formula: C₁₈H₂₃NO₅
- Purity: 99% min




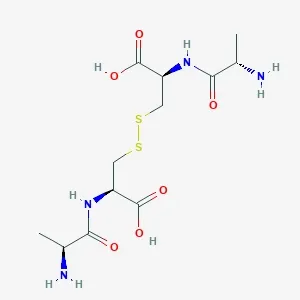
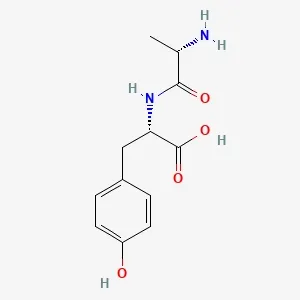
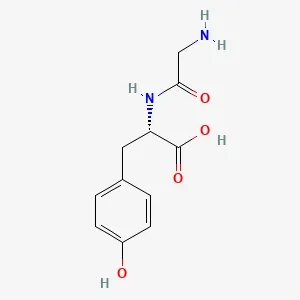
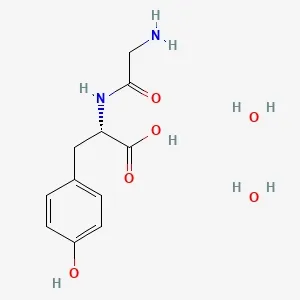
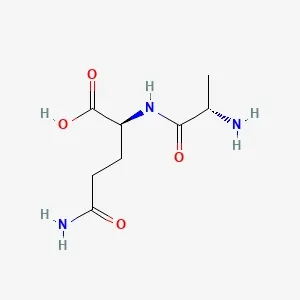
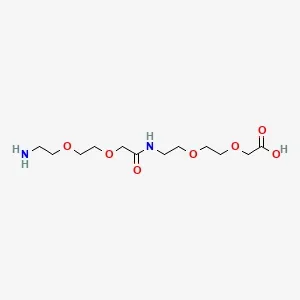
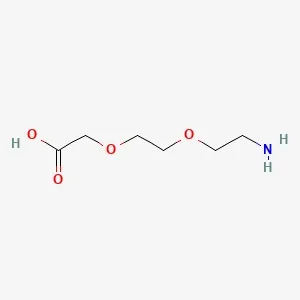
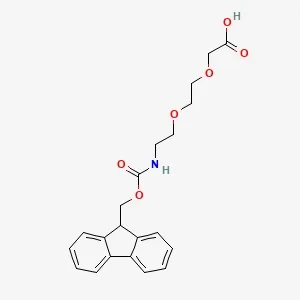
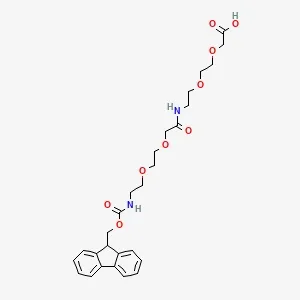
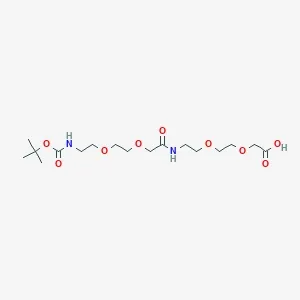
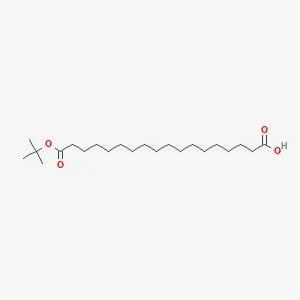
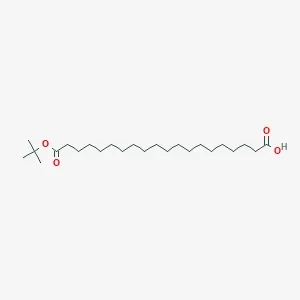
![Fmoc-L-Lys[Oct-(otBu)-γ-Glu-(otBu)-AEEA-AEEA]-OH](products/2-2-1-fmoc-l-lys-oct-otbu_01.webp)